/* ost - Solve the equation f(x) = 0 to within desired error value for x.
* Rev.3.14: Sep. 3, 2011
* Copyright(c) 1998-2011 Takayuki HOSODA, All rights reserved.
* http://www.finetune.jp/~lyuka/technote/fract/ost.html
*
* SYNOPSIS
* #include <math.h>
* #include <stdlib.h>
* #include <float.h>
*
* double
* ost(double guess1, double guess2, double (*func)(), double epsilon, double *x);
*
* RETURN VALUE
* The ost() function returns the result code, and stores a root to the x
* when it found,
* 0 : A root found.
* 1 : An approximate solution within the specified epsilon found. |f(x)| <= epsilon
* 2 : The search reached to the calculation limit. x_n+1 == x_n
* 3 : The search concentrated in a local flat region of the function. f(x_n+2) == f(x_n+1)
* 4 : The search reached to the calculation limit. |f(x_n+1)| > |f(x_n)|
* 5 : No root found while specified iteration.
* 6 : The search diverged.
* 7 : Error. Bad guess or f(x) is constant.
* 8 : Error. Bad argument, Iteration is negative.
* 9 : Error. Bad argument, func() points NULL.
* 10 : Error. Bad argument, x points NULL.
*/
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <float.h>
#ifdef DEBUG
#include <stdio.h>
#endif
#define MAXPVT 31
#define M2E31 2.147483648e9
#define EXP_THRESHOLD 1e-8
#define EXP_FACTOR -1.5
#ifndef DBL_EPSILON
#define DBL_EPSILON 2.2204460492503131E-16
#endif
double nextc(a, b) double a, b; { return a + (b - a) * (1.0 + 14.0 * ((double)random() / M2E31)) / 16.0; }
double delta(a, b) double a, b; { return b == 0.0 ? fabs(a) : (fabs(a) - fabs(b)) / fabs(b); }
double minx(a, b, c, d, e, f) double a, b, c, d, e, f; {
return fabs(f) < fabs(e) ? fabs(f) < fabs(d) ? c : a : fabs(e) < fabs(d) ? b : a;
}
int
ost(guess1, guess2, func, epsilon, iteration, x)
double guess1;
double guess2;
double (*func)(double);
double epsilon;
int iteration;
double *x;
{
double a, b, c, d, e, f, t;
int i;
int p = 0;
double q = 0.0;
double r0 = 0.0;
static double r1 = 0.0;
static double r2 = 0.0;
int xp =0;
int ft =0;
if (func == NULL) return 10;
if (x == NULL) return 9;
if (0 >= iteration) { return 8; }
a = guess1; b = guess2;
b = (a == b) ? a == 0 ? 0.01 : a * 1.01 : b;
if (0.0 == (d = (*func)(a))) { *x = a; return 0; }
if (fabs(d) <= epsilon) { *x = a; return 1; }
if (0.0 == (e = (*func)(b))) { *x = b; return 0; }
if (fabs(e) <= epsilon) { *x = b; return 1; }
c = (a + b) * 0.5; f = (*func)(c);
r2 = c; r1 = 0.0;
for (i = 0; i < iteration; i++) {
if (0.0 == f) { *x = c; return 0; }
if (fabs(f) <= epsilon) { *x = c; return 1; }
if (c == a) {
if ((p > MAXPVT) || (ft >= 2)) { *x = minx(a, b, c, d, e, f); return 2;}
ft++; p++; f = (*func)(c = nextc(a, b)); continue;
}
if (fabs(f) == INFINITY || f == NAN) {
if (p > MAXPVT) { *x = minx(a, b, c, d, e, f); return 6; }
i++; a = (a + b) * 0.5; d = (*func)(a);
p++; c = nextc(a, b); f = (*func)(c); continue;
}
if (i >= 5 && (fabs(f) >= fabs(e) * 10.0)) {
if (p > MAXPVT) { *x = minx(a, b, c, d, e, f); return 5; }
if (fabs(d) > fabs(e) * 10.0) { i++; a = (a + b) * 0.5; d = (*func)(a); }
p++; c = nextc(a, b); f = (*func)(c); continue;
}
if (ft >= 2 && xp != 3 && (fabs(f) > fabs(e)) && (EXP_THRESHOLD >= fabs(e)) && (i > p + 3)) {
*x = minx(a, b, c, d, e, f); return 4;
}
if ((f == e) || (f == d)) {
if (p > MAXPVT) {*x = c; return 7;}
if (q == 0.0) q = -fabs(b - a);
if (EXP_THRESHOLD < fabs(f)) {
if (EXP_THRESHOLD > fabs(f + f - e - d)) {
b = (f * e < 0.0) ? nextc(b, c) : b + (q *= EXP_FACTOR); e = (*func)(b); p++; continue;
}
p++; c = nextc(a, b); f = (*func)(c); continue;
} else {
q = 0.0;
}
if (f == e && DBL_EPSILON >= delta(c, a)) {*x = fabs(f) < fabs(d) ? c : a; return 2;}
if (f == d && DBL_EPSILON >= delta(c, b)) {*x = fabs(f) < fabs(e) ? c : b; return 2;}
if (ft++ >= 2) {*x = minx(a, b, c, d, e, f); return 3; }
p++; c = nextc(a, b); f = (*func)(c); continue;
}
t = e * (f - d) * (c - b) / ( d * (f - e) * (c - a));
t = (t * a - b) / (t - 1.0); /* Ostrowski's method */
if (t == c) {
if (ft >= 2) {*x = minx(a, b, c, d, e, f); return 2;}
t += (ft == 1) ? -t * DBL_EPSILON : t * DBL_EPSILON; /* finetune */
} else {
if (fabs(d) > fabs(e) && fabs(e) > fabs(f)) ft = 0.0;
}
if ( 5.0 * fabs(fabs(e) - fabs(f)) < fabs(e) + fabs(f) && f * e < 0.0) {
t = (f * b - e * c) / (f - e); /* Use regula falsi method */
} else if (0 == xp) {
r0 = r1; r1 -= (r1 / 0.53 + (c - b) / (b - a) - r2) * 0.5; r2 -= r0 * 0.5; /* IIR filter */
if ((0.5 < r2 && r2 < 1.0 && i >= 15 && EXP_THRESHOLD >= fabs(f)) && 0.01 > fabs(r1 / r2)) {
xp = 3; t = c - (c - b) * (c - b) / (c - 2 * b + a); /* Use Aitken method instead */
}
} else {
xp--;
}
a = b; b = c; c = t; d = e; e = f; f = (*func)(c);
}
*x = minx(a, b, c, d, e, f); return 5;
}
#ifdef DEBUG
#include <stdio.h>
#define ITERATION 100
#define EPSILON 2.2204460492503131E-16
double f0(x) double x; { return exp(x) - 3 * x * x; }
#ifdef DEBUG_MORE
double f1(x) double x; { return x * x * (x + 4) - 15.0; }
double f2(x) double x; { return sin(x) - x / 2.0; }
double f3(x) double x; { return exp(-x) + cos(x); }
double f4(x) double x; { return 10.0 * x * exp(-(x * x)) - 1.0 ; }
double f5(x) double x; { return atan(x) - x + 1.0; }
double f6(x) double x; { return tan(x) - 1.0 / x ; }
#endif
double f7(x) double x; { double t = x - 1.0; return (t * t * t * t * t) ; }
double
fs(x)
double x;
{
double t;
double p = 1e-5;
t = x + 273.15;
if (t < 0) return -p;
return exp(((16.635794 + 2.433502 * log(t) + 0.00001673952 * t * t) - 0.02711193 * t)
- 6096.9385 / t) * 100.0 - p;
}
int
main()
{
double root, a, b, eps;
int r;
extern double f();
printf("main:f0: exp(x) - 3 * x^2 == 0\n");
r= ost(a=3.0, b=4.0, f0, eps=EPSILON, ITERATION, &root);
printf("main:f0:[%.16g, %.16g], eps=%g, f0(%.16g) = %.16g, r=%d\n", a, b, eps, root, f0(root), r);
printf("main:f0: exp(x) - 3 * x * x == 0\n");
r= ost(a=-1.0, b=0.0, f0, eps=EPSILON, ITERATION, &root);
printf("main:f0:[%.16g, %.16g], eps=%g, f0(%.16g) = %.16g, r=%d\n", a, b, eps, root, f0(root), r);
printf("main:f0: exp(x) - 3 * x^2 == 0\n");
r= ost(a=0.0, b=1.0, f0, eps=EPSILON, ITERATION, &root);
printf("main:f0:[%.16g, %.16g], eps=%g, f0(%.16g) = %.16g, r=%d\n", a, b, eps, root, f0(root), r);
printf("main:fs: 'Water saturation pressure (Sonntag) == 1e-5'\n");
r= ost(a=-273.15, b=100.0, fs, eps=EPSILON, ITERATION, &root);
printf("main:fs:[%.16g, %.16g], eps=%g, fs(%.16g) = %.16g, r=%d\n", a, b, eps, root, fs(root), r);
printf("main:f7: (x - 1)^5 == 0\n");
r= ost(a=0.0, b=1.5, f7, eps=1e-100, ITERATION, &root);
printf("main:f7:[%.16g, %.16g], eps=%g, f7(%.16g) = %.16g, r=%d\n", a, b, eps, root, f7(root), r);
return 0;
}
#endif
|
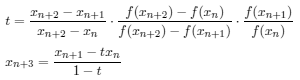
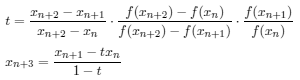
 English edition is here.
English edition is here.… (1)
… (2)
… (3)
… (6)
![[Mail]](/~lyuka/images/mail.gif)

 © 2000 Takayuki HOSODA.
© 2000 Takayuki HOSODA.